《Instance Segmentation in 3D Scenes using Semantic Superpoint Tree Networks》Paper Reading
论文信息
| 作者 | 作者单位 | 年份 | 会议/期刊名 | 引用量 | 研究方向 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kui Jia | 华南理工 华为 | 2021 | ICCV | 0 | 3D点云实例分割 |
Paper Reading
Background
作者提到之前主流方法的问题:
PointGroup第二步(聚类)过程缺少监督
Segmentation碎片化 (owing to point feature data irregularities)
Their point-wise feature learning and grouping are less effective to deal with data irregularities, possibly resulting in fragmented segmentations
Instance segmentation challenging
observed scene points are usually sparse and irregular
the unknown number of object instances in a scene introduces additional uncertainties to the problem of learning point-instance associations that is already combinatorial
learning consistencies among spatially adjacent points are not guaranteed, which may cause fragmented segmentations
Method
同样可以分成三个主要部分:
- 利用几何同源特性从点云中聚集超点
- learning a network that groups superpoints on same object instances
- refine proposal and predict score

Backbone and Semantic Scoring
网络骨架依然是U-Net
语义分割loss是CE loss加上了dice loss
这个dice loss的目的是应对类别不平衡问题alleviates the imbalance among the K categories

中心点回归loss是l2 loss加上余弦loss
Construction of Semantic Superpoint Tree
这个是本文的核心创新点
整体的流程大致是:
利用点云原始信息构建超点
利用超点对前面骨架网络推断得到的特征进行group pooling
3部分特征concat(中心点 语义分割结果 中间特征)
构建超点树 贪心策略
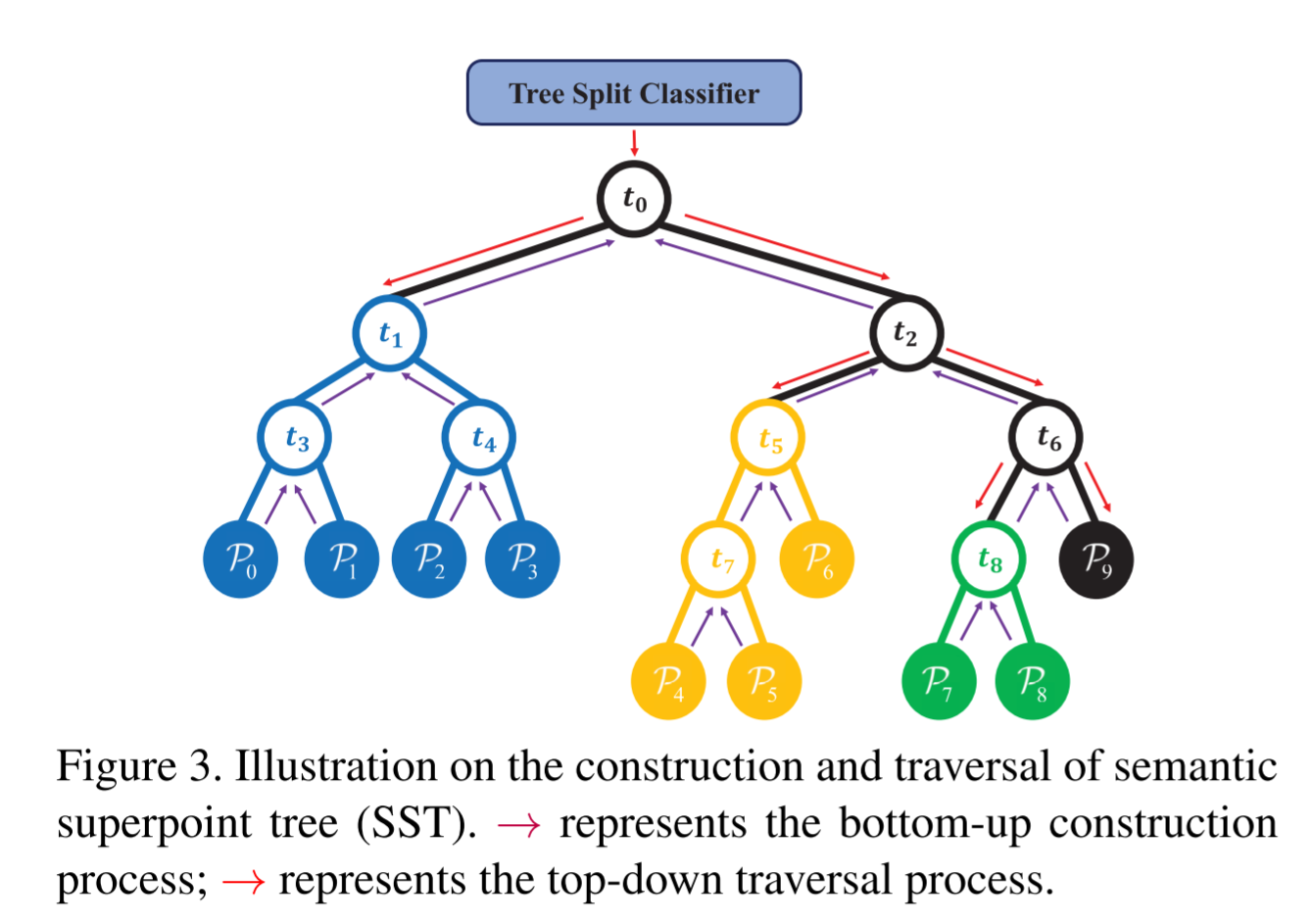
- 合并依据:语义预测向量和中心点预测向量拼起来的新向量算欧氏距离
- 合并规则:根据点的数量加权求和得到两个part的父节点的embedding centeroid semantic vector
Proposal Generation via Tree Traversal and Splitting
前面整个场景构成了一个大的超点树,每个part都是一个叶子节点,我们需要找到表示实例的节点集合,因此这里我们将从超点树中分裂出instance
具体分裂依据是计算两个节点的表示之间的相似度是否小于0.5 $\phi\left(\boldsymbol{f}{s{1}}^{\dagger}, \boldsymbol{f}{s{2}}^{\dagger}\right)<0.5$ 而这里相似度的衡量是网络学习得到的(论文中还提到了一些训练这个相似度比较网络的细节,比如:采用soft label)
CliqueNet for Refinement of Proposals
前面得到了候选instance,但是前面生成的结果的准确性不高,具体表现为:
proposed branch的semantic class有问题
proposed branch中存在小部分点是背景点或者属于其他instance
因此需要对这个proposed branch进行修剪,具体的方法看了但是真没看明白。
这部分在结果中的实际收益1个点不到,感觉很难说明该模块的有效性

Proposal Evaluation
这里就是对生成的候选实例进行得分估计,他们采用的同样是PointGroup中的ScoreNet,也没啥好说的。
Experiment
实验部分没啥特别想关注的内容
Setting
Optimizer:AdamW
两个数据集生成超点的方法不一样
问题分析
- 超点作为不可分的个体,每个instance由若干个超点构成,但是每个超点只属于一个instance。当某些场景中几何特征很难分辨两个instance的时候,这种超点构成的步骤会成为模型上限。(比如:两个桌子紧靠,两个桌子的桌子面属于一个超点)
三篇工作的总结
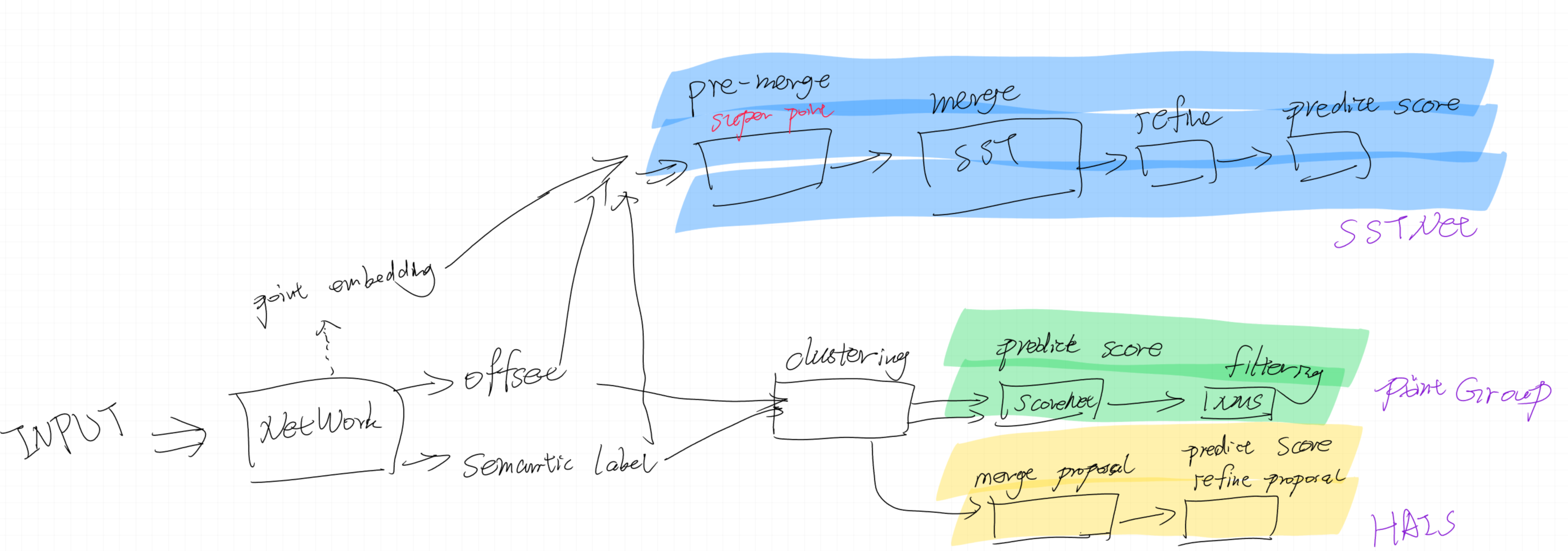
问题:
xyz+offset: 这里的offset是voxel之后得到的结果,对应的质心这里做得不太准确
上述三个流程都不是很直接,cluster+merge+filter+score比较复杂
质心坐标、语义类别、中间表示三部分很难同时使用(存在先后顺序的约束)
    - 用一个网络来聚合这几部分信息,得到一个统一的embedding
Clustering是否有更快速且性能卓越的方法?(网络学习的方式?)
先前的基于点的聚类方法的问题:没有考虑整体,只考虑点之间的邻近特性








